Difference between revisions of "Main Page"
Debra Tabron (talk | contribs) |
m |
||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
{| id="mp-left" style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; background:#f9f9f9;" | {| id="mp-left" style="width:100%; vertical-align:top; background:#f9f9f9;" | ||
| style="padding:2px;" |<h2 id="mp-tfa-h2_2" style="margin:3px; background:#cef2e0; font-family:inherit; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:center; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"><span id="#Table of Contents"></span>Table of Contents <span style="font-size:85%; font-weight:bold;"></span></h2> | | style="padding:2px;" |<h2 id="mp-tfa-h2_2" style="margin:3px; background:#cef2e0; font-family:inherit; font-size:120%; font-weight:bold; border:1px solid #a3bfb1; text-align:center; color:#000; padding:0.2em 0.4em;"><span id="#Table of Contents"></span>Table of Contents <span style="font-size:85%; font-weight:bold;"></span></h2> | ||
| − | + | {| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top;" | |
| − | {| style="width:100%; vertical-align:top;" | + | | style="vertical-align:top;" | |
| − | | | ||
<u>'''[[Transport & Attenuation Processes | Attenuation & Transport Processes]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Transport & Attenuation Processes | Attenuation & Transport Processes]]'''</u> | ||
*[[Advection and Groundwater Flow]] | *[[Advection and Groundwater Flow]] | ||
| Line 97: | Line 96: | ||
**[[Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)]] | **[[Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR)]] | ||
**[[Stable Isotope Probing (SIP)]] | **[[Stable Isotope Probing (SIP)]] | ||
| − | *[[Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume - Bemidji Crude Oil Spill]] | + | *[[Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume - Bemidji Crude Oil Spill | Natural Attenuation in Source Zone and Groundwater Plume -<br/> Bemidji Crude Oil Spill]] |
<u>'''[[Climate Change]]'''</u> | <u>'''[[Climate Change]]'''</u> | ||
Revision as of 12:47, 16 June 2020
Peer Reviewed. Accessible. Written By Experts |
Your Environmental Information Gateway |
| The goal of ENVIRO.wiki is to make scientific and engineering research results more accessible to environmental professionals, facilitating the permitting, design and implementation of environmental projects. Articles are written and edited by invited experts (see Contributors) to summarize current knowledge for the target audience on an array of topics, with cross-linked references to reports and technical literature. | See Table of Contents |
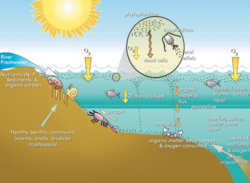
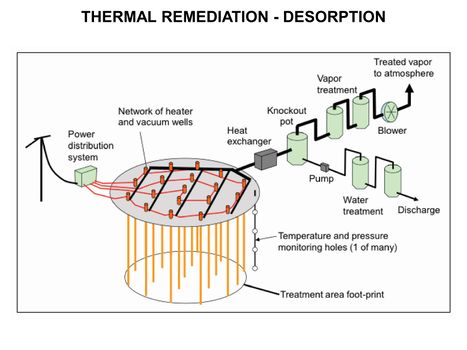
Featured article / Phytoplankton (Algae) BloomsRemoval of Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances (PFAS) from impacted soils is challenging due to the modest volatility and varying properties of PFAS compounds. Thermal treatment technologies have been developed for treatment of semi-volatile compounds such as dioxins, furans, poly-aromatic hydrocarbons and poly-chlorinated biphenyls in soils at temperatures near 325°C. In controlled bench-scale testing, removal of targeted PFAS compounds to concentrations below reporting limits was demonstrated at temperatures of 400°C. Thermal treatment temperatures of at least 400°C and a holding time of 7-10 days are recommended. The energy requirement to treat typical wet soil ranges from 300 to 400 kWh per cubic yard. Extracted vapors have typically been treated using condensation and granular activated charcoal filtration, with thermal and catalytic oxidation as another option which is currently being evaluated for field scale applications.Thermal treatment of PFAS in soils is energy intensive, and the cost of that energy may be prohibitive for some clients. Also, while it often is the least costly option for complete PFAS removal when compared to excavation followed by offsite disposal or destruction, heating soil to treatment temperatures on site or in situ typically takes longer than excavation.
(Full article...) |
Enviro Wiki Highlights |